⚗️ Electrochemical Modeling of Li-Ion Batteries
Understanding and predicting the performance, degradation, and efficiency of lithium-ion batteries requires more than just electrical circuit models. While Equivalent-Circuit Models (ECMs) provide simplified representations, they cannot capture the complex physical and electrochemical phenomena occurring inside the battery.
To address this, electrochemical models are developed based on physics-based equations that describe:
- Lithium-ion transport
- Reaction kinetics
- Charge transfer mechanisms
These models offer a detailed view of battery behavior, from the electrode particle level to the full cell.
🧪 Key Electrochemical Modeling Approaches
Several electrochemical modeling strategies are widely used, each offering a different trade-off between accuracy and computational efficiency:
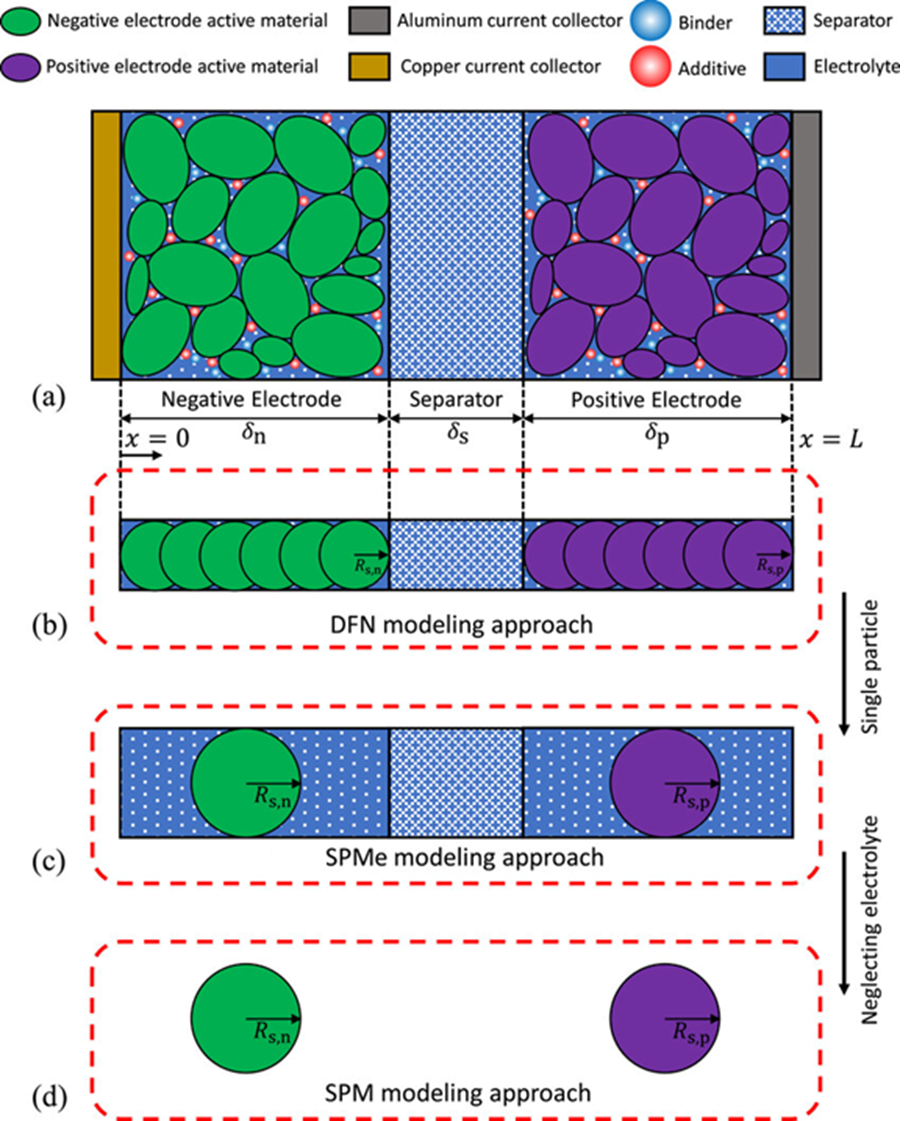
1. Doyle-Fuller-Newman (DFN) Model
- Also known as Pseudo-Two-Dimensional (P2D) or Newman Model
- Models lithium diffusion and electrochemical reactions in each active material particle (1D assumption)
- Solves a set of partial differential equations (PDEs) for both the solid and electrolyte phases
- Highly accurate, but computationally expensive
2. Single Particle Model with Electrolyte (SPMe)
- Uses a single representative particle for each electrode
- Considers lithium diffusion inside the solid and includes electrolyte concentration effects
- More efficient than DFN, with slightly reduced accuracy
3. Single Particle Model (SPM)
- Further simplification of SPMe
- Ignores electrolyte effects and models only one average particle per electrode
- Very efficient, but less accurate under high C-rate or transient conditions
🔬 Battery Cell Structure Overview
A schematic representation of a lithium-ion battery helps visualize how these models interact with physical components:
- Negative Electrode (green): Active material stores lithium during charging
- Positive Electrode (purple): Stores lithium during discharge
- Separator (blue): Prevents internal short circuits while allowing ion transport
- Electrolyte (blue with red dots): Conducts lithium ions between electrodes
- Current Collectors (gold and gray): Conduct electrons through the external circuit
🧾 Summary of Electrochemical Models
| Model | Accuracy | Efficiency | Electrolyte Effects | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DFN | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐ | ✅ Yes | High-fidelity simulation |
| SPMe | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ✅ Yes | Real-time capable with good accuracy |
| SPM | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ❌ No | Fast estimation and embedded applications |
📌 Figure: Schematic illustration of Li-ion battery chemistry (a), and electrochemical models: DFN (b), SPMe (c), and SPM (d).
🔗 Explore these models interactively at cathode.energy — your AI-powered simulation hub for Li-ion batteries!